Hotline:400-668-5636
Have you ever encountered issues with high-power devices like GPUs, HPCs, and IGBTs, such as severe overheating and performance degradation? Thermal interface materials (TIM) play a crucial role in addressing these problems. The principle behind TIM is straightforward: it reduces thermal resistance and accelerates heat dissipation by filling the air gap between the heat source and the heat sink. To help you choose the right TIM, the A lpha Pro editor has prepared a comprehensive guide. It suggests considering key factors such as the devices thermal power consumption, interface clearance, reliability requirements, and cost budget, while also evaluating the materials thermal conductivity, hardness, insulation properties, and application methods.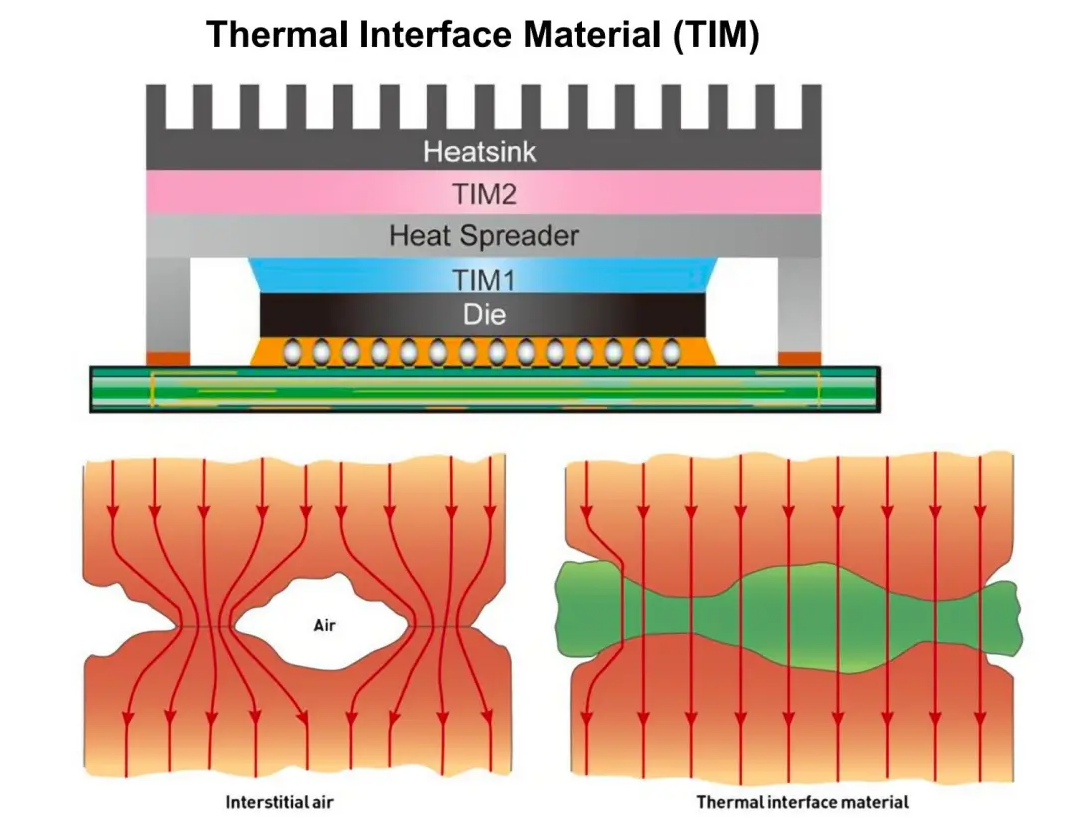
Firstly, how does TIM dissipate heat efficiently?
The heat source of electronic devices, such as chips, and the heat sink appear to be in close contact, but there are hidden complexities. Under a microscope, less than 10% of the actual contact area is visible, with the remaining 90% being filled with air. Air has an extremely poor thermal conductivity (only 0.026W/m.K), acting like a barrier to heat transfer. The core function of TIM (Thermal Interface Material) is to fill these gaps with its material, leveraging its high thermal conductivity (up to 3.5-12W/m.K), which can increase heat transfer efficiency by at least 140 times, effectively guiding heat away and preventing overheating.
Secondly, select the key indicators of TIM.
Different scenarios have different requirements for TIM, so the following indicators should be focused on when purchasing:
· Thermal conductivity (W/m · K): the higher the value, the faster the heat conduction speed. It is commonly tested by ASTM-5470 thermal plate method or ASTM-1461 laser flash method;
· Hardness: the softer the material, the easier it is to fill the gap, measured by Shore hardness meter, such as Shore 00 (soft), Shore A (hard);
· Stability: for example, the reliability of the product decreases by 5% for every 1℃ increase in temperature, so the stability directly affects the service life;
· Insulation: most scenarios require insulation, with a voltage tolerance of more than 3 KV and a dielectric constant between 3 and 10; graphene is less suitable for this scenario;
· Thermal resistance: the lower the thermal resistance, the smoother the heat transfer, is the core parameter to measure the thermal conductivity.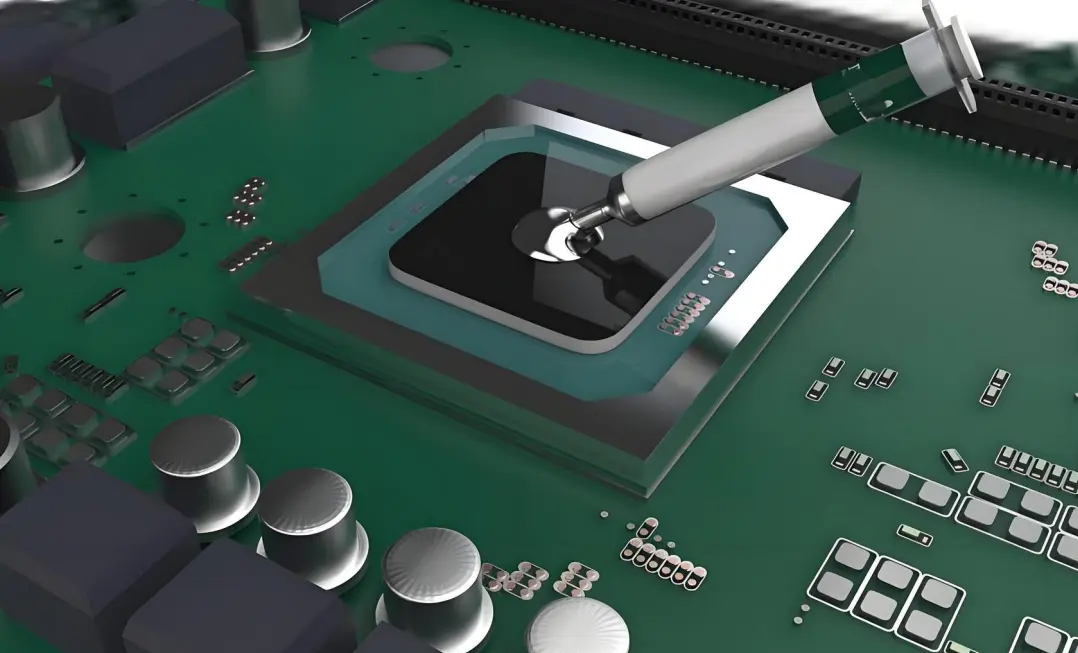
Thirdly, a general overview of common TIM materials.
There are many kinds of TIM materials on the market, from thermal grease to potting compound, each has its own expertise. Next, we will disassemble the characteristics, advantages and application scenarios of 7 commonly used thermal management materials to help you accurately match the heat dissipation needs!
Thermal Grease/
Thermal Conductive Gap Filler
🗳 Product features: Based on silicone (silicone oil), it is a fat-like compound with filler such as metal oxide powder or ceramic powder. It does not flow and meets UL 94 V-0 standard. It can cool and dissipate heat for modules such as motor or gearbox control unit
🗳 Applicable clearance: small clearance (≤0.1mm)
🗳 General parameters: thermal conductivity 2-5W/m·K; thermal resistance 0.004-0.19℃·in²/W; breakdown voltage>5KV; operating temperature-50~200℃
🗳 SWOT :
✅ Low thermal resistance, high heat flux density scene preferred, cost-effective
❌ The construction is complicated and easy to be dirty. It is easy to dry and powderize under long-term pressure and heat, and its life is about one year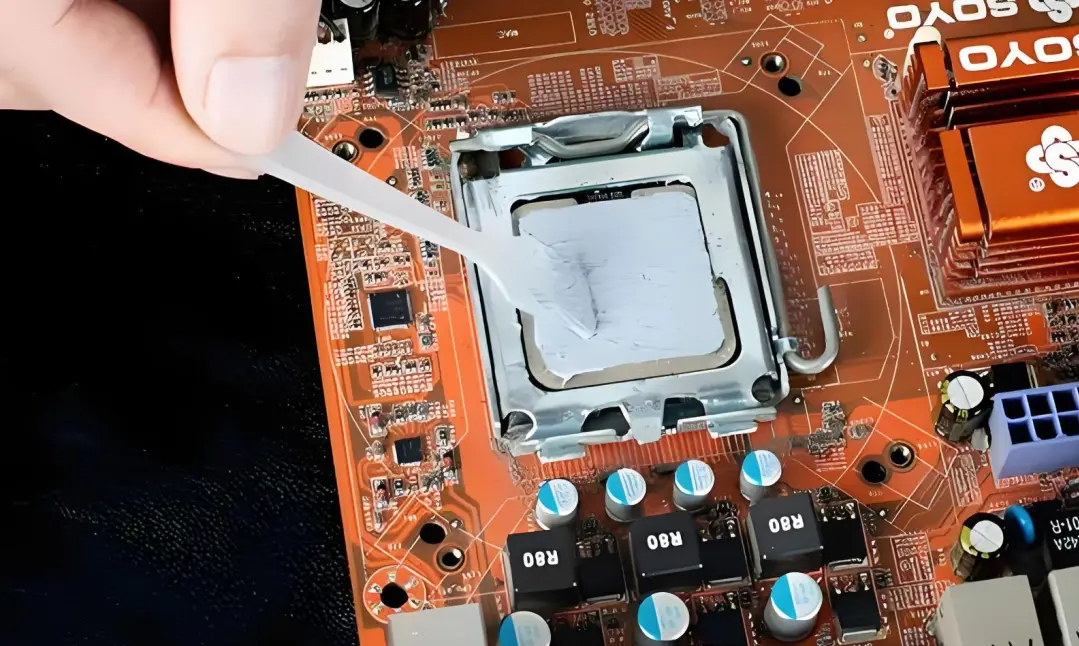
Thermal Gel/Putty
🗳 Product features: gel-like material made of silicone composite thermal filler, strong plasticity
🗳 Applicable clearance: medium and low clearance (0.2-0.5mm)
🗳 General parameters: thermal conductivity 3~12W/m·K, thermal resistance 0.04~0.19℃·in²/W, breakdown voltage 3~10KV, operating temperature-50~200℃
🗳 SWOT :
✅ Excellent joint filling performance, no stress, no curing, life of 5-8 years
❌ The heat transfer coefficient is limited and not suitable for high heat flux density scenarios
Thermal Pad
🔖 Product features: silicone base material + metal oxide, soft self-adhesive, both insulation and shock absorption function
🔖 Applicable gap: 0.2-3 .0 mm
🔖 General parameters: thermal conductivity 1~5W/m·K, thermal resistance 0.05~0.2℃·in²/W, breakdown voltage>8KV, compression rate 100%-150%
🔖 SWOT :
✅ Easy to be cut and processed, strong stability, life of more than 10 years, wide applicability
❌ It cannot produce thickness below 0.2mm, so it is not suitable for small gap scenarios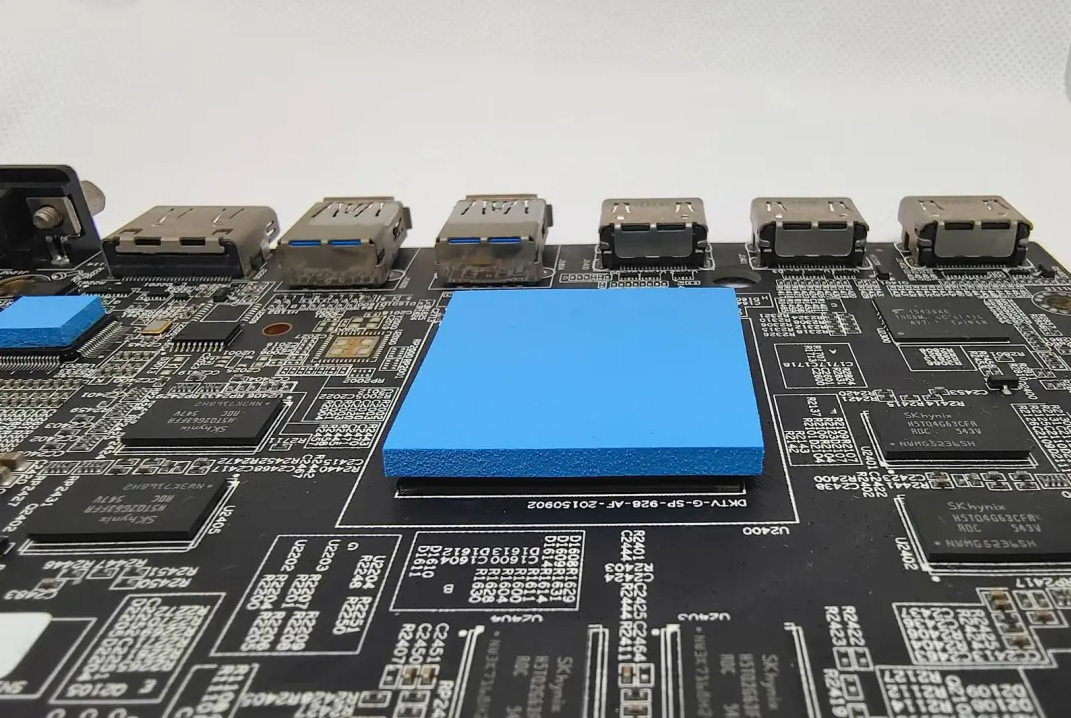
Phase Change Thermal Pad
🗳Product features: the shape changes with temperature, solid at room temperature, sticky and easy to assemble; when the phase change temperature (40-55℃) is reached, it becomes soft and fills, with good wettability and low thermal resistance
🗳 Applicable gap: 0.1 5~0.50 mm
🗳 General parameters: thermal conductivity 3~8W/m·K, thermal resistance 0.005~0.035℃·in²/W, operating temperature-45~12 5℃
🗳 Advantages and disadvantages:
✅ It integrates the operability of silicone sheet with the low thermal resistance characteristics of silicone grease, and combines PI film or aluminum foil substrate for temperature overshoot protection
❌ The price is high, and the requirements for uniform force and storage conditions are harsh
Thermal Management Tape
🔖 Product features: thermal acrylic + thermal ceramic powder, strong adhesive composite structure. Can be attached to heat source or heat dissipation materials, such as 5G millimeter wave antenna installation and fixation, heat pipe, from MLB / FPC to the radiator, other components in LED electronic equipment
🔖 Applicable gap: 0.050~0.50mm
🔖 General parameters: thermal conductivity 0.3~0.6W/m·K, thermal resistance 0.5~5℃-in²/W, pressure resistance>6KV, long-term temperature-20~100℃
🔖 SWOT :
✅ Strong adhesion to replace screws, easy to process, life of 3-5 years (80-100℃)
❌ The contradiction between heat conduction and adhesion, not reusable, thermal resistance is large
Thermal Potting Compound
💡 Product features: the liquid is fluid when not solidified, and can achieve waterproof, heat conduction, insulation and other functions after solidification
💡 Application gap: no specific limit
💡 Standard parameters: thermal conductivity 0.6~2.0W/m·K (customizable 4W/m·K), temperature resistance-40~250℃, single/double component
💡 Advantages and disadvantages: ✅Multi-functional protection, different materials (silicone/epoxy/polyurethane) to meet multiple needs
❌ The curing process is required, and the cost and performance of different categories are different
Thermal Foam
🔖 Product features: foam base composite thermal conductive material (graphite/copper foil, etc.), high compressibility. It can be used for electrical components and battery packs support, shock absorption, dustproof, moisture-proof sealing and other scenarios
🔖 Applicable clearance: large clearance (>5mm)
🔖 General parameters: thermal conductivity 3~15W/m·K, compression ratio 150%-300%, common thickness 5.0~20mm, temperature resistance-60~2 30℃
🔖 Advantages and disadvantages:
✅ High cost performance in large gap scenes, flexible design, smooth surface suitable for special installation
❌ The whole edge packaging process is complex, and there is no advantage in performance and cost below 3mm
Application scenario: the role of high performance thermal mud in intelligent projector
In intelligent projectors, a large amount of heat is generated when the projector works, especially the chip. Heat dissipation problems are common. In order to ensure the normal operation of the chip and prolong the service life of the product, more and more scenarios will consider thermal conductive mud. The hardness of the chip is low, and it can form the minimum interface thermal resistance with increasing pressure, which helps improve the heat conduction efficiency.
The motherboard CPU chip and inductor element of a well-known projector product use A lpha P roTMThermal conductive mud 5403 is directly connected to the heat sink. Compared to traditional thermal pads, thermal conductive mud can better fill gaps between non-planar surfaces. It has better plasticity compared to silicone grease, making it more suitable for filling larger gaps. This material excels in interface filling, forming a continuous thin layer on the surfaces of chips and inductors, ensuring a seamless and tight bond with the heat sink, thus enhancing heat transfer efficiency.
Conclusion: From low thermal resistance thermal grease to thermal foam suitable for large gaps, each material is protecting the stable operation of the equipment. However, there is no "standard answer" for heat dissipation solutions, and the requirements of TIM vary greatly in different scenarios.
What challenges have you faced with heat dissipation in electronic devices? Have you encountered issues like the chip cooling down and reducing frequency, or the stability problems that arise after prolonged use? Feel free to share your pain points or success stories in the comments! Follow A lpha Pro Erfa New Materials for more professional heat dissipation knowledge and customized solutions, ensuring every bit of heat finds its optimal escape route!